Orion and the Ocean of Storms
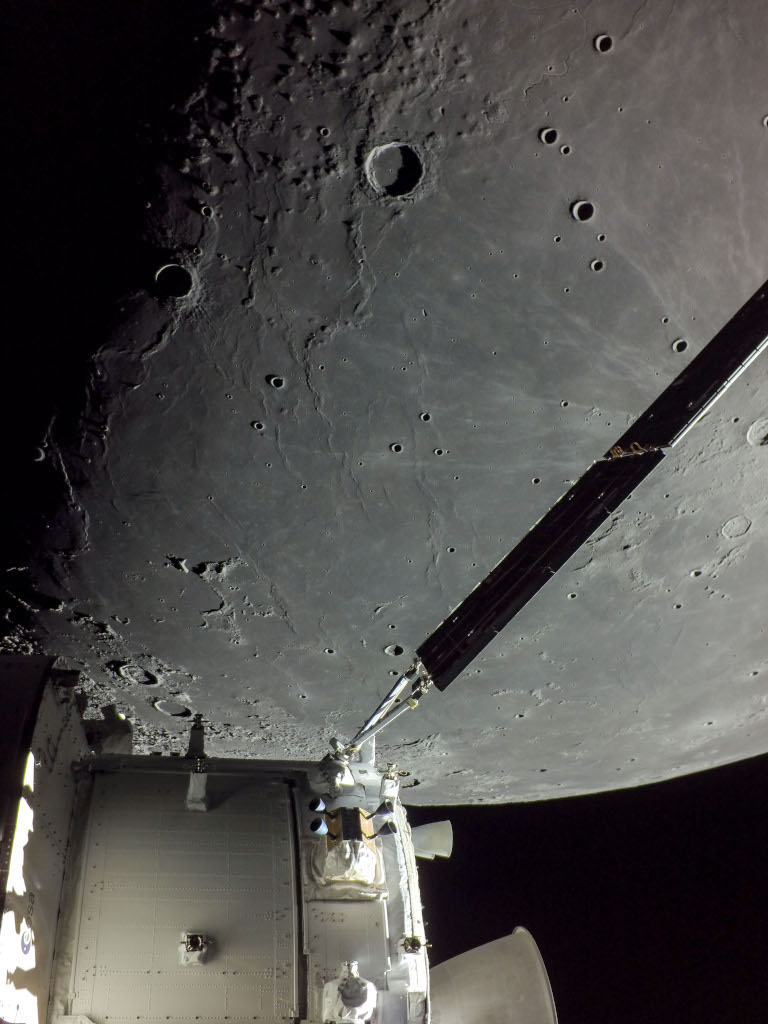
On December 5, 2022, a camera on board the uncrewed Orion spacecraft captured this view as Orion approached its return powered flyby of the Moon. Beyond one of Orion's extended solar arrays lies dark, smooth, terrain along the western edge of the Oceanus Procellarum. Prominent on the lunar nearside Oceanus Procellarum, the Ocean of Storms, is the largest of the Moon's lava-flooded maria. The lunar terminator, the shadow line between lunar night and day, runs along the left of this frame. The 41 kilometer diameter crater Marius is top center, with ray crater Kepler peeking in at the edge, just right of the solar array wing. Kepler's bright rays extend to the north and west, reaching the dark-floored Marius. By December 11, 2022 the Orion spacecraft had returned to its home world. The historic Artemis 1 mission ended with Orion's successful splashdown in planet Earth's water-flooded Pacific Ocean. Watch: The Geminid Meteor Shower